Blog
Cloud Phone System
What Is PBX? A Complete Guide to PBX Phone Systems

What Is PBX? A Complete Guide to PBX Phone Systems
Discover what PBX is, how it has evolved from traditional systems to cloud solutions, and how it is now part of broader cloud-based business tools.
When it comes to business communication, a reliable phone system is essential. PBX has been a cornerstone of office telephony for decades, enabling employees to connect internally and manage external calls efficiently. But what exactly is PBX, how has it evolved, and why is it still relevant in today’s cloud-driven world?
PBX systems have come a long way from manual switchboards and analog hardware to fully virtual cloud solutions. Today, many businesses are moving to modern internet-based phone systems that offer greater flexibility, advanced features, and seamless connectivity.
In this guide, we’ll explore the meaning of PBX, trace its evolution over time, and see its role in modern cloud phone systems.
What is PBX Phone System?
What Does PBX Stand For?
PBX stands for Private Branch Exchange; a private telephone network used within a company. It enables employees to communicate internally across different phones connected to the same network while also managing external calls efficiently.
A Brief History of PBX
The story of PBX begins in the 1960s, when businesses faced major challenges with traditional telephone infrastructure. At that time, all calls had to go through manual switchboards at telephone companies, making call management slow, complicated, and expensive.
To solve this, businesses started building internal switchboards, creating their own mini telephone networks. This approach reduced call queues, lowered operating costs, and allowed companies to customize call routing, including forwarding calls between departments.
The landscape of business communication shifted dramatically with the rise of the internet. By the mid-2000s, VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol) technology emerged, allowing voice communication to travel over internet networks as data packets instead of traditional phone lines. This innovation also made PBX systems virtual, giving rise to cloud-based PBX solutions.
Let’s take a closer look at the different types of PBX, their evolution, and how they compare.
Types of PBX Phone Systems
Over the years, PBX systems have evolved significantly, moving from on-premises hardware to fully virtual cloud platforms. Each type has its own advantages and limitations. Here’s a detailed look at the main PBX models and how they compare.
Traditional Analog PBX
The earliest PBX systems, known as traditional analog PBX, were fully on-premises. These hardware-based systems relied on copper wiring and manual switchboards, connecting internal phones while linking offices to the Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN). They allowed employees to create internal extensions, transfer calls, and route communications between departments.
Analog PBX provided reliable control over office communications, but installing and maintaining these systems was expensive. They offered limited flexibility and scalability, and expanding the system to multiple office locations required complex leased lines or T1/E1 connections. While businesses could create multi-site setups, doing so involved significant infrastructure and cost, which often drove the move to digital solutions.
IP PBX
With the rise of VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol) in the 2000s, IP PBX systems emerged as the next generation of business telephony. Unlike analog PBX, IP PBX uses Internet Protocol to transmit voice as data packets instead of relying solely on copper phone lines. Internal calls typically remain within the office network (Ethernet), while external calls can leverage VoIP connections via SIP trunks or other internet services.
IP PBX systems can be installed on dedicated hardware appliances or run as software on standard PCs or servers. Companies remain responsible for maintaining the equipment, which may require a server room, backup power, and technical support.
Compared to analog PBX, IP PBX offers significantly more flexibility and advanced functionality.
Hosted PBX
Hosted PBX represents a shift from managing hardware on-site to outsourcing telephony infrastructure to a third-party provider. In the early days, this primarily meant that the provider managed the PBX hardware, reducing the need for businesses to install and maintain complex systems themselves.
The main advantage of hosted PBX is the reduced reliance on on-site hardware, which lowers upfront costs and accelerates deployment. Companies no longer needed in-house engineers for setup or maintenance, though some physical phones or adapters were sometimes still required. Providers handled system updates, scaling, and infrastructure management, making hosted PBX a more flexible and cost-effective solution than on-premises setups.
Today, the term hosted PBX often overlaps with cloud hosted PBX systems, because both rely on infrastructure hosted in the cloud and are accessed entirely over the internet.
Cloud-Based PBX
Cloud-based PBX is a fully virtual phone system that runs entirely in the cloud. Users can make and receive calls over the internet using IP desk phones or software apps on desktops and mobile devices. This model eliminates the need for extensive on-site hardware, offers easy scalability, and provides a rich set of business features. Cloud PBX delivers flexibility, remote access, and simplified management, making it ideal for modern businesses of all sizes.
You might have heard cloud PBX referred to as hosted PBX, virtual PBX, or simply as a hosted phone system, however, nowadays, they all generally mean the same thing.
Hybrid PBX
Hybrid PBX combines elements of traditional on-premises systems with cloud solutions. It allows businesses to maintain their existing hardware while integrating cloud features and VoIP capabilities through SIP trunking or cloud extensions. This model provides the benefits of both worlds: the control and reliability of on-site equipment, alongside the flexibility, scalability, and advanced features of cloud technology. Hybrid PBX is particularly useful for large enterprises or organizations with significant legacy investments in PBX infrastructure, allowing them to gradually transition to the cloud without disrupting existing operations.
Today, in business communications, the terms cloud PBX, hosted PBX, and VoIP phone systems generally refer to cloud-based platforms that enable businesses to manage both internal and external communications.
Why Do Businesses Choose Cloud PBX?
Cloud-based PBX systems have become the go-to solution for businesses of all sizes because they combine flexibility, cost efficiency, and advanced functionality in a single platform.
- Scalability: Hosted in the cloud, these systems can support everything from a small team to thousands of employees across multiple offices or countries. Adding new users or extensions is simple and doesn’t require additional hardware, making it ideal for growing businesses.
- Cost savings: Without the need for traditional copper lines or extensive on-site equipment, companies can reduce phone bills and eliminate costly maintenance. Cloud PBX also minimizes upfront investment, allowing businesses to pay only for the features and users they need.
- Flexibility and mobility: Employees can make and receive calls from desktops, laptops, or mobile devices using just an internet connection. This ensures teams stay connected wherever they are and supports seamless remote or hybrid work.
- Easy setup and minimal maintenance: Cloud PBX can be up and running in just a few days, with software updates and infrastructure management handled automatically by the provider. This relieves internal teams from technical headaches while delivering a reliable, modern, and feature-rich communication system.
Key Features of Cloud PBX Phone Systems for Small Businesses
Cloud PBX systems provide businesses with essential call management tools, forming the backbone of modern communication. At their core, they handle traditional phone system functions, ensuring that calls are managed efficiently and professionally.
Every Cloud PBX includes the core features you’d expect from a business phone system:
- Multiple phone lines: Cloud PBX allows businesses to have multiple phone numbers for different departments, locations, or employees, all managed through the same system. The system can handle multiple calls at once using VoIP channels, ensuring that teams never miss a call, even during high-traffic periods.
- Auto-attendant / IVR (Interactive voice response): Auto-attendant systems or IVR menus greet callers automatically and guide them through options such as “Press 1 for Sales, 2 for Support.” This reduces the need for live receptionists, ensures calls reach the right department, and creates a professional, consistent caller experience.
- Call queues: Call queues manage incoming calls when all agents are busy, placing callers in line and providing custom hold music or announcements. This ensures callers stay informed and engaged until the next available agent can assist them.
- Call transfers: Call transfer allows employees to seamlessly redirect calls to another team member, department, or external number. This feature ensures that calls reach the right person without interrupting workflow or customer experience.
- Conference calling: Cloud PBX enables multiple participants to join a single call, making team collaboration and group discussions simple and efficient.
- Voicemail: Voicemail captures messages from missed calls, ensuring no communication is lost.
Beyond Basic Cloud PBX: Advanced Cloud Phone Systems
If you’re a modern startup or small business looking for a phone system for daily communications, you might wonder how Cloud PBX relates to the various cloud phone platforms available today. Basically, modern cloud phone systems are built on top of Cloud PBX. They include all the essential call management tools of a Cloud PBX but extend them to a whole new level.
Platforms like DialLink not only offers all the standard Cloud PBX features but also provide advanced capabilities like:
- Advanced call routing and management: Configure business hours and routing rules to ensure every call reaches the right person at the right time.
- AI-powered call automation: Use AI voice agents to manage inbound and outbound calls, reducing manual workload and improving response times.
- AI call intelligence: Organize calls and gain actionable call insights with automated call tagging, summaries, transcripts, sentiment analysis, and action items to reduce manual workload.
- Advanced voicemail: Receive transcriptions and voicemail-to-email notifications, ensuring you never miss important messages.
- Omnichannel support: Manage all customer interactions from a single platform, including calls, SMS, and WhatsApp, ensuring a seamless experience across channels.
- CRM and app integrations: Sync call data and customer interactions with Salesforce, HubSpot, Zendesk, and other applications to keep your team informed and workflows connected.
- Multi-device flexibility: Access the platform from desk phones, mobile devices, or desktop apps, enabling employees to stay productive from anywhere.
- Local and global phone numbers: Establish a professional presence with local, toll-free, or international numbers.
- Number porting: Easily transfer existing phone numbers to your cloud system without service interruptions.
- Analytics & reporting: Monitor call volume, missed calls, agent performance, and other key metrics to make informed, data-driven decisions.
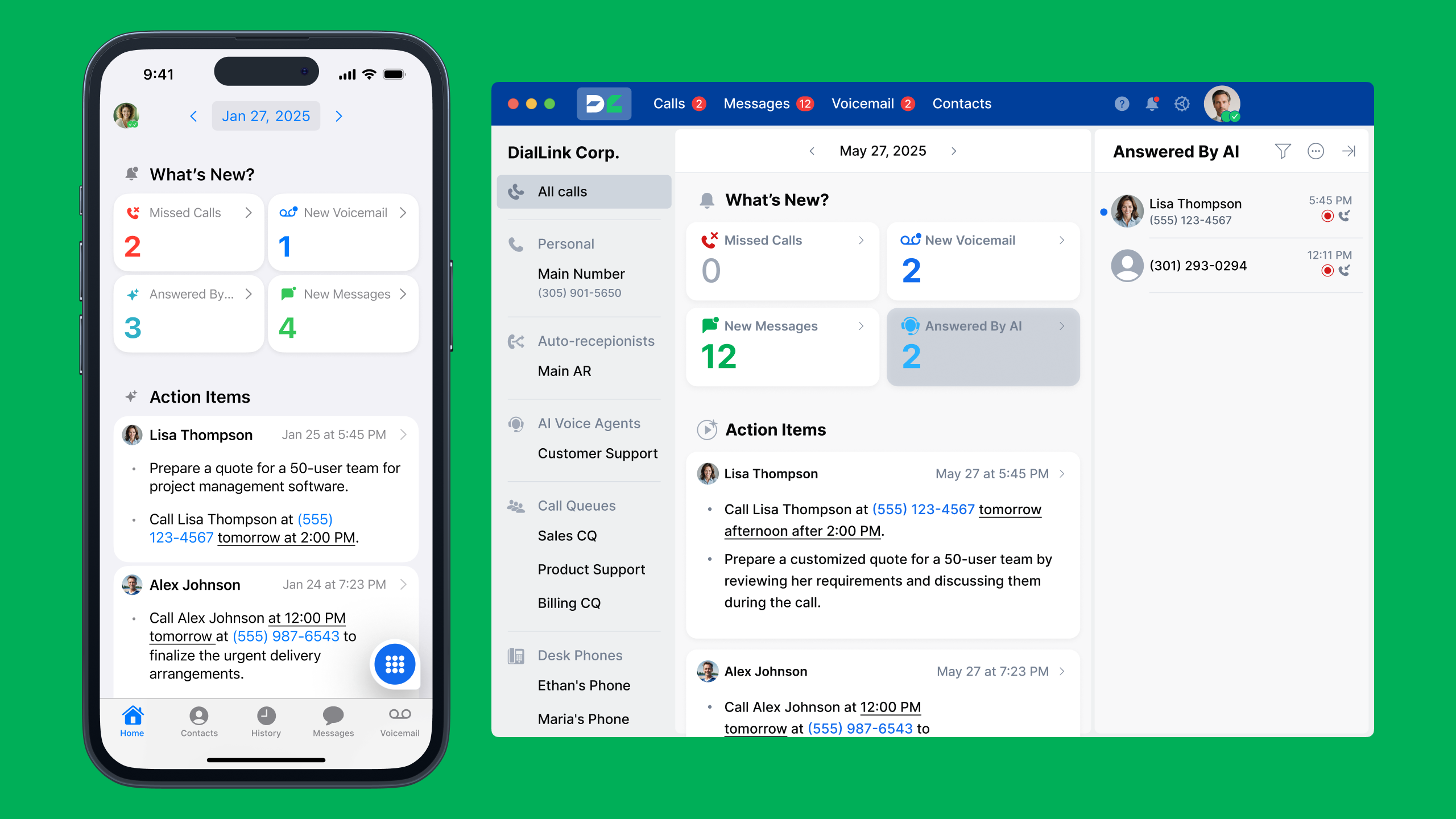
Conclusion: Cloud PBXs or Advanced Phone Systems?
For years, Cloud PBX systems have been the backbone of business communication, offering a reliable, scalable, and cost-effective way to manage calls. They are easy to set up, accessible, and ideal for small businesses looking for a straightforward phone solution.
Today, advanced cloud phone systems like DialLink provide a compelling alternative. These platforms combine all the essential PBX features with enhanced capabilities such as business messaging, AI-powered automation, and advanced call management, enabling small businesses to streamline communication, improve collaboration, and deliver a more professional customer experience.
Need a phone system that’s more flexible and adaptable than PBX? Try DialLink today.
PBX stands for Private Branch Exchange, meaning it is a private telephone network that businesses use to manage internal calls between employees and external calls through the public telephone network.
PBX, or Private Branch Exchange, is a phone system that manages how calls are routed within a business. It handles extensions, voicemail, call transfers, and other telephony features. Traditionally, PBX systems relied on physical hardware and landlines, but modern versions such as IP PBX or Cloud PBX now operate over the internet.
VoIP, or Voice over Internet Protocol, is different in that it is a technology rather than a system. Instead of using copper phone lines, VoIP transmits voice calls over the internet, enabling lower costs, greater flexibility, and support for remote communication.
The cost of a PBX system depends on the type you choose. A traditional on-premises PBX comes with high upfront expenses, often ranging from $1,000 to more than $10,000 depending on the size of the company. On top of the hardware, businesses must account for ongoing maintenance, IT staff, upgrades, and additional fees for phone lines or international calling.
An IP PBX, which is VoIP-enabled but still hosted on-site, lowers call costs because it uses the internet rather than copper lines. However, it still requires servers and IT management. Hardware and licensing fees can start at a few hundred dollars and reach several thousand, depending on the deployment.
A cloud PBX, hosted by a provider, is the most flexible and cost-effective option for many SMBs. Pricing is typically subscription-based, ranging from $15 to $40 per user each month. There are no hardware or maintenance costs, and scaling is simple — you just add or remove users as needed.
Featured Tags
Share

Arina Khoziainova
Content Writer at DialLink
Arina is a content writer with over 7 years of experience in the IT industry. At DialLink, she creates clear, insightful content that helps small business and startup owners simplify communication and drive growth using modern tools. With a strong focus on practical value, Arina transforms complex topics into accessible, actionable stories.
Keep Reading

What Is a Hunt Group and How Do Small Businesses Use It for Smart Call Routing?
Learn what a hunt group is, how it works, how it differs from other call routing features, and how to set one up to reduce missed calls and improve response times.

What is an Inbound Call Center? A Complete Guide for Small Businesses and Startups
Learn what an inbound call center is, how it differs from outbound call centers, and when outsourcing might be the right choice for your small business.
What Is a Business Phone System? A Complete Guide for SMBs and Startups
Discover what a business phone system is, how it works, and which modern phone systems are best for small businesses and startups.
Types of Business Phone Systems: Cloud, VoIP, PBX & More
Discover different types of business phone systems, how they differ, and which options may be the best fit for your business.

Google Voice Business Phone System: Features, Pricing, and Limitations for Small Businesses
Learn how the Google Voice business phone system works, explore plans, features, and limitations for small businesses and startups.

Auto Attendant Message Examples and Scripts for Small Businesses
Find a list of auto attendant message examples, samples, and scripts that you can use for your small business phone system.

Auto Attendant Recordings: Examples, Samples and Best Practices for Small Businesses
Explore auto attendant recording examples, samples, and tips for small businesses and startups to create professional phone greetings.

Best Auto-Attendant Systems & Services for Small Businesses
Explore the best auto attendant systems and software for small businesses. Learn features, types, and top providers.