
Text-to-Speech and Speech-to-Speech: How Each Can Benefit Your Business?
Explore both technologies that power AI voice agents, their pros and cons, and how to choose the best fit for your business needs.
It’s no surprise that AI agents can “speak” today. From Siri answering questions to AI-generated audiobook narrators, and even support bots in online stores, AI is increasingly capable of handling voice conversations.
However, not all voice AI works the same way.
Behind the scenes, different technologies power these systems. The most common are text-to-speech (TTS) and the newer, emerging speech-to-speech (STS).
Both technologies allow AI agents to communicate through voice, but they operate in different ways, and each with unique strengths and limitations.
In this article, we’ll look at what each technology is, how they enable AI voice agents, where they are used, and their respective pros and cons. We’ll also discuss how to choose the right option for your business needs.
What Are AI Voice Agents? And How Are They Used?
AI voice agents are intelligent conversational systems that use human-like speech to communicate with people.
They are increasingly common in both personal and business settings. In daily life, you might interact with them through virtual assistants on smartphones or smart speakers. In business, they are widely adopted as customer support assistants, sales tools, or virtual receptionists.
As virtual receptionists, AI voice agents go far beyond legacy IVR systems that rely on rigid menus and prerecorded prompts. Instead, they can engage in dynamic, intelligent conversations, understanding customer intent and responding in real time.
Their strongest impact has been in customer service, where they are proven to handle routine queries effectively and automate repetitive tasks. With the rise of MCP servers, their capabilities are expanding even further, enabling them to book appointments, provide order status updates, and perform other business-specific actions by connecting directly to backbone systems.
Now, let’s take a closer look at the technologies behind applications known as “AI voice agents.”
How Does Text-to-Speech AI Voice Agents Work?
First, let’s look at the technology that powers text-to-speech (TTS) AI voice agents.
What is Text-to-Speech Technology?
Text-to-speech (TTS) is a type of speech synthesis that converts written text into spoken voice output. In other words, it’s the technology that allows a computer or device to “read aloud” text in a human-like voice.
TTS was originally developed as an assistive tool, for example, to help people with visual impairments or reading difficulties by reading digital text aloud. Over time, the technology has advanced significantly and become common in everyday applications. Today, you encounter TTS when a GPS navigation system reads directions aloud or when an e-book app narrates a story. Popular virtual assistants, such as Apple’s Siri, Amazon’s Alexa, and Google Assistant, also rely on TTS to deliver spoken responses. Essentially, TTS gives applications and devices a “voice,” enabling more natural, hands-free interactions.
Early TTS technologies were typically rule-based or pieced together prerecorded snippets of audio, resulting in robotic and unnatural-sounding voices. Modern TTS systems, by contrast, combine natural language processing (NLP) with advanced audio generation techniques to create speech that is far more fluid, expressive, and human-like.
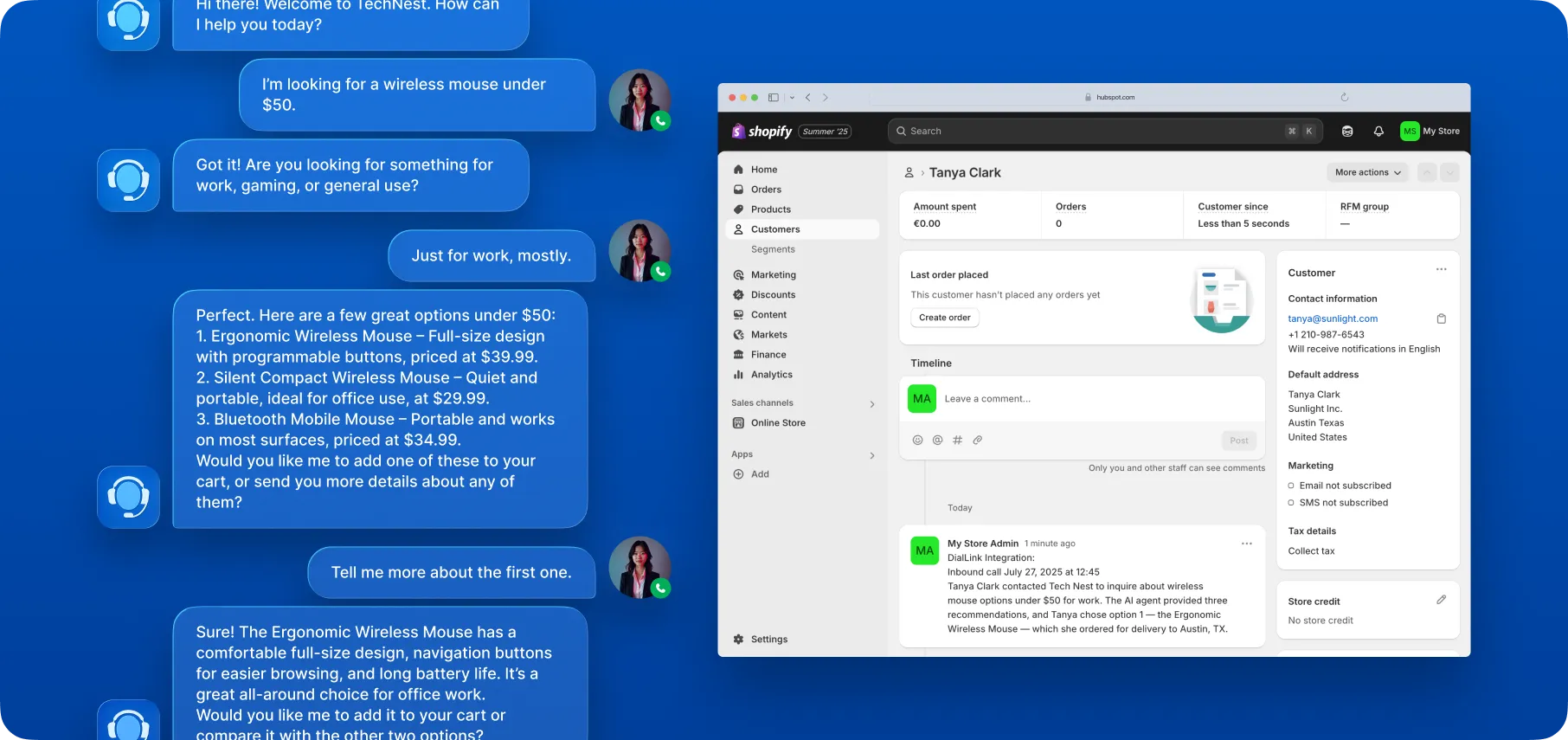
How Do Text-to-Speech AI Voice Agents Work Behind the Scenes?
While TTS is often seen as the core technology, it usually operates as part of a more traditional STT → LLM → TTS pipeline:
- STT (Speech-to-Text): Converts spoken audio into text — the “ears” of the system.
- LLM (Large Language Model): Processes the transcribed text and generates a response — the “brain” of the system.
- TTS (Text-to-Speech): Converts the response back into spoken audio — the “voice” of the system.
In this sequence, TTS is responsible for the “last mile” of communication, delivering the AI agent’s response in natural-sounding speech.
How Does Speech-to-Speech AI Voice Agents Work?
AI voice technology is evolving and moving beyond the traditional text-driven pipeline. Instead of always converting speech into text and then back into audio, new systems can handle conversations in a more direct and natural way.
What is Speech-to-Speech Technology?
Speech-to-speech (S2S), sometimes called voice-to-voice technology, is an approach where an AI system takes spoken audio as input and produces spoken audio as output without ever relying on text. In simple terms, an S2S voice agent can listen to what you say and respond with a spoken reply.
When OpenAI introduced its Realtime API, it enabled seamless speech-to-speech interactions using prebuilt voice presets. This marks a shift toward multimodal AI systems capable of interpreting audio input, generating a response, and producing audio output in real time, all while taking into account context such as tone, pacing, or user emotion.
Although speech-to-speech technology is still developing, it holds great promise for creating more fluid, natural, and human-like interactions, making it a major step forward in conversational AI.
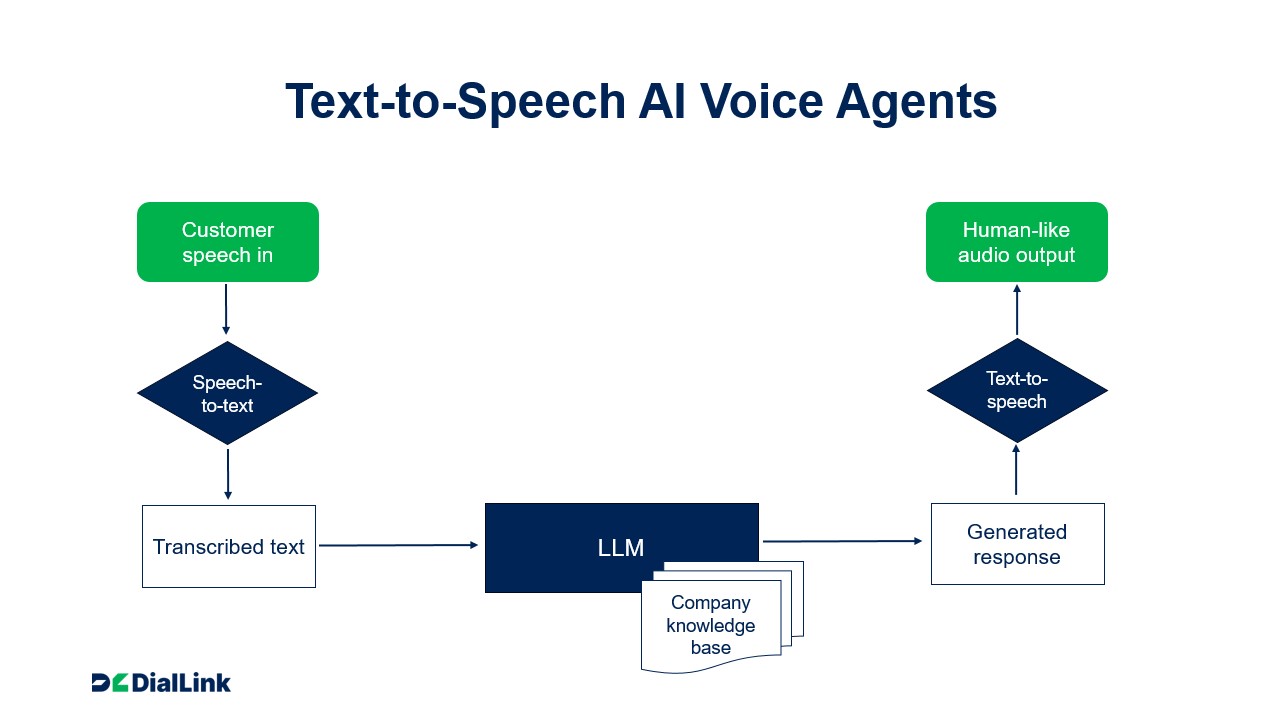
How Do Speech-to-Speech AI Voice Agents Work Behind the Scenes?
Unlike the old-school STT → LLM → TTS pipeline, many new multimodal models include speech-to-speech, or functionalities very close to it, by consolidating these functions into a single process and eliminating the need for multiple technologies working in sequence.
Here’s a simplified view of how it works:
- Audio input: The system receives a user’s spoken input.
- End-to-end processing: A multimodal model interprets the speech directly, extracting meaning, intent, and emotional cues.
- Audio output: The system generates a spoken response immediately, without converting the input into text first.
Considerations for Text-to-Speech AI Voice Agents
TTS is still the most widely used technology for enabling AI agents to have a voice. It is mature, cost-effective, and supported by a wide ecosystem of tools and providers. However, like any technology, it comes with trade-offs. Below, we’ll look at both the advantages and limitations of TTS in AI voice agents.
Pros of text-to-speech
-
Wide variety of voice options: One of the key strengths of TTS is its ability to provide a broad selection of voices, covering different genders, accents, and tones.
Modern TTS platforms typically include extensive voice libraries, allowing businesses to choose voices that reflect their brand personality and customer expectations. Some systems even support voice cloning or custom voice synthesis, enabling organizations to design a unique branded AI voice that reinforces their identity.
In addition, parameters such as speech speed, pitch, and intonation can often be adjusted. This flexibility helps create more natural, engaging speech that feels tailored to the audience and enhances the overall customer experience.
-
Strong multilingual and regional support: TTS systems offer broad language coverage, often including multiple dialects and regional variations. This makes it possible for companies to serve global audiences effectively and adapt voice agents for local markets.
-
Flexible and LLM-agnostic: TTS systems are highly flexible and can integrate with a wide range of Large Language Models (LLMs). An LLM-agnostic setup means developers can use fine-tuned models or switch to new ones as technology evolves. Since the LLM functions as the “brain” of the agent, this flexibility ensures the system remains adaptable as more advanced models become available.
-
Cost-effective and accessible: TTS is one of the most cost-effective approaches for voice AI. Numerous ready-made solutions are available, which reduces the need for businesses to build each component from scratch. This makes TTS a practical entry point for organizations looking to deploy AI-powered voice agents without heavy upfront investment.
Limitation of text-to-speech
- Very limited emotion and expressiveness: Although TTS has improved significantly, it still struggles with natural expressiveness. Emotional tone, empathy, and subtle conversational dynamics are often missing, making interactions feel less human-like.
- Higher response latency: Because TTS usually operates in a sequential pipeline, converting audio input to text (STT), processing it with an LLM, and then converting it back to audio, the process introduces noticeable delays. Response times typically range between 0.7 and 3 seconds, which can disrupt the flow of natural conversation.
- Less adaptive to natural speech dynamics: TTS systems can struggle to capture the nuances of human conversation. They may sound too rigid when handling interruptions, overlapping speech, or shifts in tone and pacing. Unlike natural speakers who adjust rhythm and emphasis based on context, TTS outputs often remain uniform, which can make interactions feel less responsive and engaging in real-world conversations.
- Mispronunciations and errors: TTS agents may mispronounce uncommon words, acronyms, or names. They can also produce awkward outputs if the text input contains typos or unusual phonetic spellings. This limits their adaptability in real-world conversations.
- Technical complexity and integration challenges: Building stable TTS-based AI systems often requires managing multiple technologies in sequence (STT → LLM → TTS). This layered setup increases the risk of technical instability and makes fallback mechanisms essential to ensure the system can handle errors gracefully.
Considerations for Speech-to-Speech AI Voice Agents
Speech-to-speech (S2S) technology offers a powerful new approach to building AI voice agents. By consolidating the traditional STT → LLM → TTS pipeline into a more direct process, S2S enables more natural and engaging interactions. However, as with any emerging technology, it comes with both advantages and challenges.
Pros of speech-to-speech
- Enhanced emotional expressiveness: One of the most remarkable capabilities of S2S-enabled AI voice agents is their ability to deliver far more natural speech than traditional TTS systems. Most of the modern models can preserve emotional cues, rhythm, and tone, allowing voice agents to sound more human-like and empathetic. This creates conversations that feel much closer to speaking with a real person.
- Lower latency and faster responses: By streamlining the process into an end-to-end model, S2S AI agents eliminate the need to convert speech into text and then back into audio. This results in quicker responses and more seamless back-and-forth dialogue.
- Smoother conversational flow: Because responses are faster and more natural, S2S-enabled AI agents maintain smoother conversational flow, significantly improving the overall user experience.
- Built-in multilingual translation support: While TTS offers broader language coverage overall, S2S agents excel at real-time translation. They can listen in one language and respond in another with minimal delay, offering more fluid multilingual interactions within their supported language range than traditional TTS systems.
Limitation of speech-to-speech
- Limited voice customization features: Unlike TTS, which offers large voice libraries and advanced features like voice cloning, S2S currently provides fewer options for voice style. However, as the technology rapidly evolves, its customization options are expected to expand.
- Dependence on specific LLMs: Most S2S-enabled AI voice agents are built tightly around end-to-end models, which means you cannot easily swap or upgrade the underlying LLM.
- Higher deployment and usage costs: S2S requires more computational power and advanced infrastructure, making it more expensive to deploy and maintain compared to TTS-based systems. In addition to infrastructure costs, businesses may also face higher ongoing expenses when using commercial S2S AI voice agents' services, as real-time audio processing and low-latency performance typically demand more premium pricing tiers.
- Potential data privacy concerns: Unlike many TTS solutions, which can often be deployed in region-specific cloud environments or even on-premises, most S2S systems require user audio to be processed and stored on the vendor’s servers. This reduces control over where sensitive data is handled and increases compliance risks.
Business Use Cases of Using Both Types of AI Voice Agents
Both TTS and S2S-enabled AI voice agents have a wide range of applications in business. TTS is best for structured, one-way information delivery, while S2S shines in dynamic, conversational scenarios. Below are examples of how organizations can put each to work.
Business Use Cases of Text-to-Speech AI Voice Agents
TTS voice agents are most effective when the goal is to deliver information at scale without requiring fluid, back-and-forth conversation. In these cases, small delays are acceptable, and the main focus is consistency and efficiency.
Automated Customer Support (IVR Systems)
Businesses use TTS to power IVR menus and self-service bots that provide basic information, such as account balances, shipping updates, or store hours. This reduces pressure on human agents while ensuring customers get essential details quickly.
Outbound Notifications and Alerts
Banks, airlines, and healthcare providers rely on TTS to deliver time-sensitive updates, including fraud alerts, flight changes, or appointment reminders. These notifications are automated, consistent, and can reach large customer bases efficiently.
Sales and Marketing Outreach
TTS can generate personalized voice messages for outbound campaigns, customer follow-ups, or promotional announcements—without the cost of hiring voice talent for every variation.
Training and Internal Communications
Organizations convert written materials, such as compliance manuals, onboarding guides, or HR updates, into audio using TTS. This allows employees to consume content while multitasking, improving knowledge retention and flexibility.
Public Announcements
Airports, train stations, and retail stores use TTS to broadcast announcements such as boarding calls, safety instructions, or promotional offers. This ensures consistent delivery across multiple locations.
Internal Productivity Bots
Within organizations, TTS agents can connect to CRMs, ticketing systems, or scheduling platforms, turning spoken commands into real-time data queries. For example, a manager might say, “What’s the status of our top 10 open support tickets?” and the agent could respond with up-to-date information verbally. This reduces the need to navigate dashboards, improving productivity and decision-making speed.
Business Use Cases of Speech-to-Speech AI Voice Agents
As AI voice agents evolve beyond simply reading out information, they are becoming independent assistants capable of handling more complex and dynamic processes for businesses. Unlike TTS-based systems, which are best for one-way information delivery, S2S agents enable fluid, real-time conversations that feel far closer to human interaction. This makes them especially valuable in customer-facing roles and high-stakes business scenarios.
AI-Powered Virtual Receptionists
S2S-enabled receptionists can greet callers naturally, ask follow-up questions to clarify intent, gather key details, and route calls dynamically. This makes them a far more human-like alternative to rigid IVR menus. Instead of forcing customers through layered “press 1 for sales, press 2 for support” options, an S2S receptionist can understand requests like “I’d like to check on an invoice” and warm transfer the call seamlessly.
Tier-1 Customer Support Assistant
S2S AI voice agents can manage routine customer inquiries through natural, conversational interactions. They can listen to customer concerns, provide relevant information, and suggest solutions without sounding scripted. When MCP-enabled, these agents go a step further by pulling data from business systems and performing actions on behalf of the business, such as checking order status, updating account details, or scheduling an appointment. Their ability to respond without delays and dynamically adapt to the flow of conversation makes them highly effective Tier-1 customer support specialists, reducing workload for human agents while maintaining a positive customer experience.
Conversational Sales Assistants
Retailers and e-commerce businesses can deploy S2S agents as real-time sales assistants that engage customers in natural, human-like conversations. These agents can answer pre-sales questions, guide shoppers through purchase decisions, recommend complementary products, and even upsell in a conversational style. Unlike static chatbots, S2S agents can dynamically interact with customers, helping them add or remove items from a cart, update delivery preferences, apply discounts, or confirm order details. This creates a more personalized shopping experience while driving higher conversion rates and average order values.
Real-Time Multilingual Support
For global businesses, S2S agents can translate speech on the fly, enabling them to serve customers across multiple regions without expanding support teams for every language. For example, a European retailer can provide customer service in Spanish, French, and German simultaneously, while an American SaaS provider could support Latin American and Asian markets without hiring bilingual agents. This is particularly valuable in travel and international e-commerce sales.
Choosing Between Text-to-Speech and Speech-to-Speech AI Voice Agents for Your Business
When deciding whether to deploy TTS or S2S-enabledAI voice agents, the right choice depends on your business goals, budget, and customer experience priorities.
When To Choose Text-to-Speech AI Voice Agents
- Best for structured, predictable interactions: TTS works best in scenarios where conversations don’t need to feel fluid or deeply personalized, such as IVR menus, automated announcements, outbound notifications, and FAQ-style interactions.
- Voice branding matters: With rich voice libraries and cloning options, TTS enables businesses to design a branded voice identity that reflects their personality and strengthens customer recognition.
- Need for cost-effective solution: TTS solutions are widely available, affordable, and fast to implement, making them a strong option for businesses that need a reliable voice channel without heavy investment.
Best fit for: Use cases that require cost-effective AI automation for routine structured communications, without the need for highly personalized or natural conversations. Examples include appointment reminders, delivery status updates, and confirmations.
When to Choose Speech-to-Speech AI Voice Agents
- Customer-facing processes require human-like interactions: S2S AI voice agents enable more natural, expressive conversations that closely mirror human interaction, making them ideal for businesses that compete on customer experience.
- Supporting complex, high-stakes processes: In industries such as healthcare, banking, or hospitality, customers expect more than scripted answers. S2S agents can guide users through detailed scenarios, such as verifying sensitive information or resolving urgent problems, while sounding confident and responsive.
- Serving multilingual audiences in real time: Global companies can use S2S agents to provide customer service across multiple regions with real-time translation. This reduces the need for large multilingual support teams and ensures smoother cross-border interactions.
Best fit for: Use cases that demand natural and complex conversations, where customers expect more than scripted responses and need guidance through detailed, context-rich interactions. Examples include basic technical troubleshooting, scheduling or reservation appointments, and insurance claims assistance with policy guidance.
When a Hybrid Approach Works Best
Because business needs are rarely one-dimensional, the smartest strategy is often not choosing between TTS and S2S but combining them. Each technology excels in different scenarios, and together they can create a balanced, future-ready voice strategy.
For instance, companies can use TTS to handle routine, predictable interactions such as IVR menus, appointment reminders, or account updates. These tasks demand reliability and cost efficiency, which TTS delivers at scale. At the same time, S2S-enabled AI voice agents can act as autonomous assistants for customer support and sales, managing dynamic conversations and handling complex inquiries.
By blending TTS and S2S, businesses can achieve the best of both worlds: cost control through automation and scalability, and customer satisfaction through natural, responsive voice experiences where they matter most.
Conclusion
Choosing between text-to-speech and speech-to-speech voice AI ultimately depends on your business needs, budget, and the type of customer experience you want to create. TTS is reliable and scalable for routine tasks, while S2S enables natural, real-time conversations for high-value interactions.
Each approach has its own strengths and limitations. In practice, the smartest strategy often lies in combining both, using TTS for routine, predictable tasks and S2S for high-value, customer-facing conversations.
And when both technologies are available in a single platform, the possibilities expand even further. With DialLink, you don’t have to choose between TTS and S2S. Our platform supports both, giving your business the freedom and flexibility to have AI voice agents that are flexible, cost-effective, scalable, and capable of supporting all your use cases while elevating your customer experience.
Moreover, DialLink’s business phone system not only provides built-in AI voice agents but also offers a robust set of advanced call management features, unified business texting and WhatsApp messaging, and AI-powered call intelligence.
Text-to-speech (TTS) converts written text into synthetic speech, giving machines a human-like voice for reading scripts or responses. Speech-to-speech (S2S) takes spoken input and generates spoken output directly, often preserving tone and style or even translating into another language. In short: TTS makes machines talk, while S2S makes them converse like humans.
One of the biggest limitations of TTS is latency, since it has to process text and then convert it into speech, responses can sometimes feel slower. In addition, TTS voice agents often sound less natural and expressive compared to S2S-enabled agents.
Yes, speech-to-speech is generally more natural, making interactions feel smoother and more human-like. In comparison, TTS still tends to sound flat or overly consistent, even in advanced systems, because it lacks the ability to capture the tone, rhythm, and emotional nuance of real speech.
Both types of AI voice agents are valuable for customer service, they just serve different use cases:
- TTS is better for predictable, scripted responses such as FAQs, automated announcements, and IVR menus.
- S2S is better for interactive conversations where empathy, tone, and quick responses matter.
Absolutely. Many companies deploy TTS for static or repetitive content and S2S for dynamic conversations (like troubleshooting, sales calls, or live translations). Combining both helps balance cost-efficiency with customer experience quality.
Yes. S2S excels in multilingual contexts because it can translate spoken input and output speech in another language. This makes it ideal for global call centers, travel services, or businesses that serve international customers.
TTS typically introduces a slight delay as text is processed into speech, but it’s optimized for near real-time responses. S2S in end-to-end models can reduce latency by generating spoken replies directly from audio input. This results in faster, more natural back-and-forth conversations, closer to human dialogue.
Featured Tags
Share
In this article
- What Are AI Voice Agents? And How Are They Used?
- How Does Text-to-Speech AI Voice Agents Work?
- How Does Speech-to-Speech AI Voice Agents Work?
- Considerations for Text-to-Speech AI Voice Agents
- Considerations for Speech-to-Speech AI Voice Agents
- Business Use Cases of Using Both Types of AI Voice Agents
- Choosing Between Text-to-Speech and Speech-to-Speech AI Voice Agents for Your Business
- Conclusion

Arina Khoziainova
Content Writer at DialLink
Arina is a content writer with over 7 years of experience in the IT industry. At DialLink, she creates clear, insightful content that helps small business and startup owners simplify communication and drive growth using modern tools. With a strong focus on practical value, Arina transforms complex topics into accessible, actionable stories.
Keep Reading

Artificial Intelligence Calls: Definition, Examples, and How It Works
Learn what artificial intelligence calls are, how they work, and how your business can benefit from using AI-powered voice calling solutions.

How DialLink Leverages MCP to Streamline AI Integrations
Discover how DialLink leverages MCP to connect AI Voice Agents with AI models and business tools, enabling them to solve real business challenges.

What Is MCP? A Guide to Model Context Protocol
Discover what Model Context Protocol (MCP) is, how it works, and why it’s revolutionizing AI voice agents, call automation, and integrations for SMBs and startups. Learn key benefits, detailed use cases, and future trends.
5 Ways AI Appointment Setters Streamline Your Business
Discover how AI appointment setters streamline your business by answering calls, automatically booking appointments directly into your calendar, and capturing lead data.

Adapt or Fall Behind: The Truth About Conversational AI for Small and Medium Businesses
Cut through the AI hype and explore the real-world benefits small businesses can achieve today with conversational AI.

How AI Voice Works: A Simple Guide to the Tech Behind AI Calls (And Why It’s Not Sci-Fi Anymore)
Read a comprehensive breakdown of how AI voice agents work, explained in simple terms, but grounded in serious technology.

AI Voice Agents 101: A Simple Guide for Small Business and Startup Owners
Discover how AI voice agents help small businesses and startups answer calls, capture leads, and assist customers using the latest AI technology.

Conversational AI in Insurance: Enhancing Claims & Customer Support
Discover the leading conversational AI in insurance solutions — from intelligent chatbots to AI voice agents — that streamline claims, enhance customer support and reduce costs.